Question 6:
Diagram below shows a straight line RS with equation 3y = –px – 12, where p is a constant.
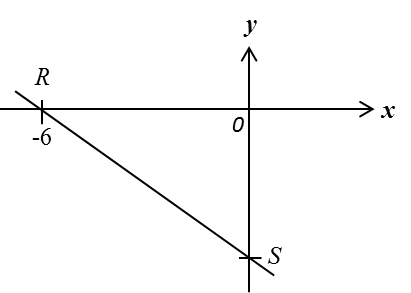
It is given that OR: OS = 3 : 2.
Find the value of p.
Solution:
Method 1:
Substitute x= –6 and y = 0 into 3y = –px – 12:
3(0) = –p (–6) – 12
0 = 6p – 12
–6p = –12
p = 2
Method 2:
OR: OS = 3 : 2
OROS=326OS=32OS=6×23=4units
Coordinates of S = (0, –4)
Gradient of the straight line RS =
−−4−6=−23
Given 3y = –px – 12
Rearrange the equation in the form y = mx + c
Question 7:
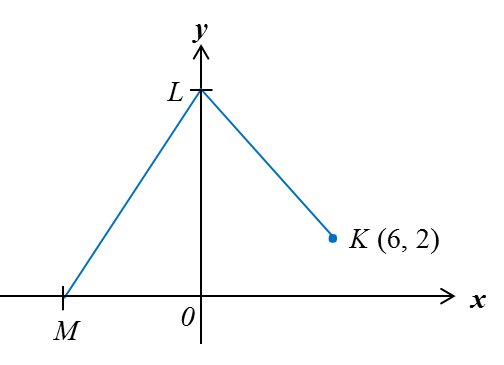
The above diagram shows two straight lines, KL and LM, on a Cartesian plane. The distance KL is 10 units and the gradient of LM is 2. Find the x-intercept of LM.
Solution:
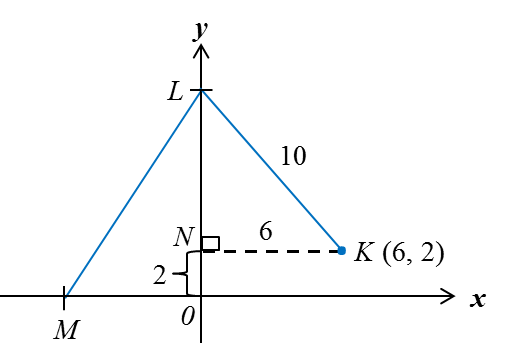
Let point N be = (0, 2).
Using Pythagoras’ Theorem,
LN = √102 – 62 = 8
Point L = (0, 2 + 8) = (0, 10)
y-intercept of LM = 10
Using the gradient formula,m=−y-interceptx-intercept2=−(10x-intercept)x-intercept ofLM=−102=−5