Example 1:
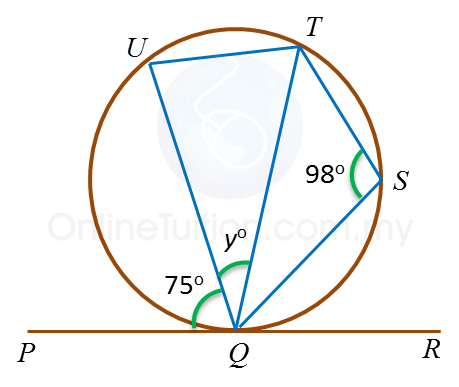
In the diagram, PQR is a tangent to the circle QSTU at Q.

Find the value of y.
Solution:
Angle QUT
= 180o– 98o ← (opposite angle in cyclic quadrilateral QSTU )
= 82o
Angle QTU = 75o ← (angle in alternate segment)
Therefore y= 180o – (82o + 75o) ← (Sum of interior angles in ∆ QTU)
= 23o
Example 2:
In the diagram, PQR is a tangent to the circle QSTU at Q.
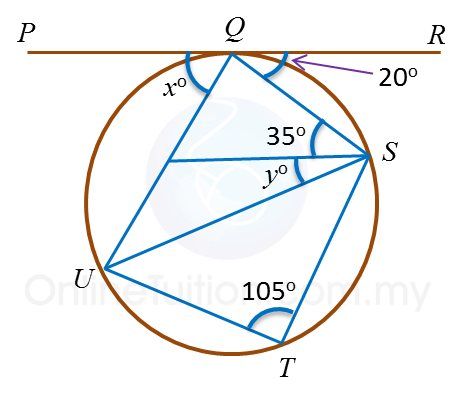

Find the values of
(a) x (b) y
Solution:
(a)
∠UTS + ∠UQS = 180o ←(opposite angle in cyclic quadrilateral QSTU)
105o + ∠ UQS = 180o
∠ UQS = 75o
x+ 75o + 20o = 180o←(the sum of angles on a straight line PQR = 180o)
x+ 95o = 180o
x = 85o
(b)
∠ PQU = ∠ QSU ← (angle in alternate segment)
85o = 35o + y
y = 50o Example 3:
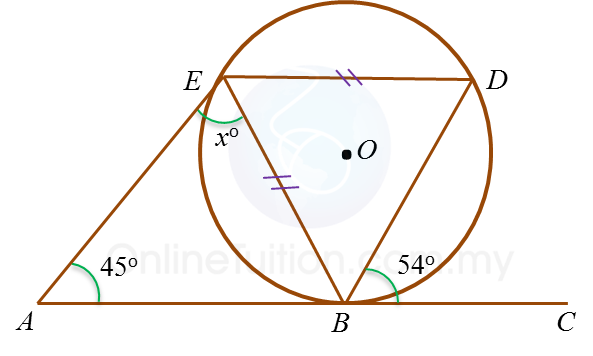

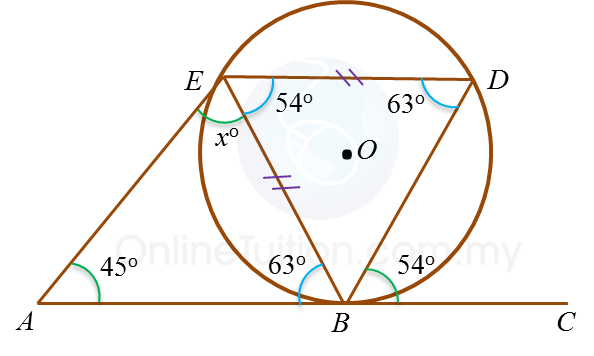
In the diagram, ABC is a tangent to the circle BDE with centre O, at B.
Find the value of x.
Solution: